During the fall semester I came across the concept of specifications grading. We had a faculty member interested in trying it out, and another professor who was already using a version of it in his courses. For today’s post, I’d like to give an overview of specifications grading with resources to turn to for more information.
 Specifications grading is not a brand new concept. In the spring of 2016, both Inside Higher Ed and The Chronicle of Higher Education ran articles on this grading method. The Inside Higher Ed piece, Yes, Virginia, There’s a Better Way to Grade (January 19, 2016) was written by Linda Nilson, who authored the seminal work on the concept: Specifications Grading: Restoring Rigor, Motivating Students, and Saving Faculty Time (Stylus Publishing, 2015).
Specifications grading is not a brand new concept. In the spring of 2016, both Inside Higher Ed and The Chronicle of Higher Education ran articles on this grading method. The Inside Higher Ed piece, Yes, Virginia, There’s a Better Way to Grade (January 19, 2016) was written by Linda Nilson, who authored the seminal work on the concept: Specifications Grading: Restoring Rigor, Motivating Students, and Saving Faculty Time (Stylus Publishing, 2015).
Nilson starts her book, which is a relatively short read (131 pages of text), by giving an overview of the history of grading. While the origins of our university system goes back to the 6th century, grading students is a more recent idea, first appearing in the 1700s and becoming more formalized in the 19th century. There is little standardization across institutions and practices vary considerably. Nilson notes that grading on the curve, grade inflation, and interpretations attached to grades further complicate the practice, leading to a system that she characterizes as broken and damaging to both faculty and students. Moreover, it is not at all clear that grades are an accurate predictor of future success.
Nilson contends there is a better system (see summary pp. 129-131), i.e., specifications grading (also called specs grading), which will:
- Uphold high academic standards,
- Reflect student learning outcomes,
- Motivate students to learn,
- Motivate students to excel,
- Discourage cheating,
- Reduce student stress,
- Make students feel responsible for their grades,
- Minimize conflict between faculty and students,
- Save faculty time,
- Give students feedback they will use,
- Make expectations clear,
- Foster higher-order cognitive development and creativity,
- Assess authentically,
- Achieve high interrater agreement,
- Be simple.
Her grading construct, which can be adapted in part or fully (as she explains in detail in her book), relies on pass/fail grading of assignments and assessments, the structuring of course content into modules linked to learning outcomes, and the bundling of assignments and assessments within those modules. The completion of course modules and bundles is linked to traditional course grades. In the pure form of specs grading, students determine what grade they want and complete the modules and bundles that correspond to that grade.
Nilson provides a summary of the features of specifications grading (p. 128):
- Students are graded pass/fail on individual assignments and tests or on bundles or modules of assignments and tests.
- Instructors provide very clear, detailed specifications (specs)—even models if necessary— for what constitutes a passing (acceptable/ satisfactory) piece of work. Specs reflect the standards of B-level or better work.
- Students are allowed at least one opportunity to revise an unacceptable piece of work, or start the course with a limited number of tokens that they can exchange to revise or drop unacceptable work or to submit work late.
- Bundles and modules that earn higher course grades require students to demonstrate mastery of more skills and content, more advanced/ complex skills and content, or both.
- Bundles and modules are tied to the learning outcomes of the course or the program. Students will not necessarily achieve all the possible outcomes, but their course grade will indicate which ones they have and have not achieved.
Nilson’s article in Inside Higher Ed referenced above, gives a quick overview to specifications grading basics. It’s a good starting place to determine if the concept holds appeal for you. While any new system of teaching, including grading, will have a learning curve, specs grading offers a great deal of flexibility. In her book, Nilson gives examples of ways to partially integrate the concept into your course planning. It is also clear that once implemented, the system saves faculty time in making “hairsplitting decisions” about how many points to award on an assignment or test. Rubrics are required, but they are based on a satisfactory/unsatisfactory set of criteria, rather than spelling out what is expected for a full range of grades. Yes, faculty must be transparent and up front about this system with the students, but the anecdotal experiences that Nilson shares in her book indicate that students find specs grading to be less stressful and more motivating than traditional methods.
I recommend reading Nilson’s full book to understand the nuances and to determine which aspects of the system you will want to employ. To give you a sense of the scope of the book, following is an outline of the chapters and material covered.
Chapter 1: Introduction to and history of grading, and rationale for a new grading system.
Chapter 2: Discussion of learning outcomes and course design.
Chapter 3: Linking grades to outcomes—covers Bloom’s Taxonomy and how specs grading works in this regard.
Chapter 4: The efficacy of pass/fail grading.
Chapter 5: Details of specifications grading with detailed examples, including the role of rubrics, and adding flexibility through the use of tokens and second chances.
Chapter 6: How to convert specs graded student work to final letter grades. This chapter explains the concept of modules and bundling as related to levels of learning and grades that will be earned as modules/bundles are completed.
Chapter 7: Examples of specifications-graded course design. Nilson presents nine case studies from a variety of disciplines that include the types of activities and assessments that can be used.
Chapter 8: How and why specs grading motivates students—this chapter examines theories and research on student motivation to build a case for specs grading.
Chapter 9: Detailed instructions for developing a course with specs grading. This chapter includes tips for a hybrid course model that combines elements of specs grading with traditional grading constructs, and ideas for introducing students to specs grading.
Chapter 10: Conclusion and evaluation of specifications grading.
I also want to mention the article in The Chronicle of Higher Education, Prof Hacker Blog, Experimenting with Specifications Grading, Jason B. Jones, March 23, 2016, which reports on an instructor’s experience with specifications grading. It links to this blog post Rethinking Grading: An In-Progress Experiment, February 16, 2016, by Jason Mittell, who teaches at Middlebury College. The first-hand experience will be enlightening to those considering specs grading. Mittell includes the statement on his syllabus explaining specs grading to students, which will help you formulate your own explanation for this important part of a successful implementation of specs grading. You should also be sure to read the comments on the Prof Hacker piece for some additional ideas and resources.
As always, I am interested in comments from those who have tried or are considering this idea. Please share your thoughts.
Macie Hall, Senior Instructional Designer
Center for Educational Resources
Image Source: Pixabay.com

 Our last two posts have focused on diversity and inclusion in the classroom. Today I’d like to offer some resources for another important way to create a positive classroom climate: knowing your students’ names and pronouncing them correctly. A previous post
Our last two posts have focused on diversity and inclusion in the classroom. Today I’d like to offer some resources for another important way to create a positive classroom climate: knowing your students’ names and pronouncing them correctly. A previous post 





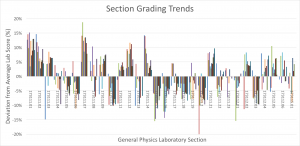
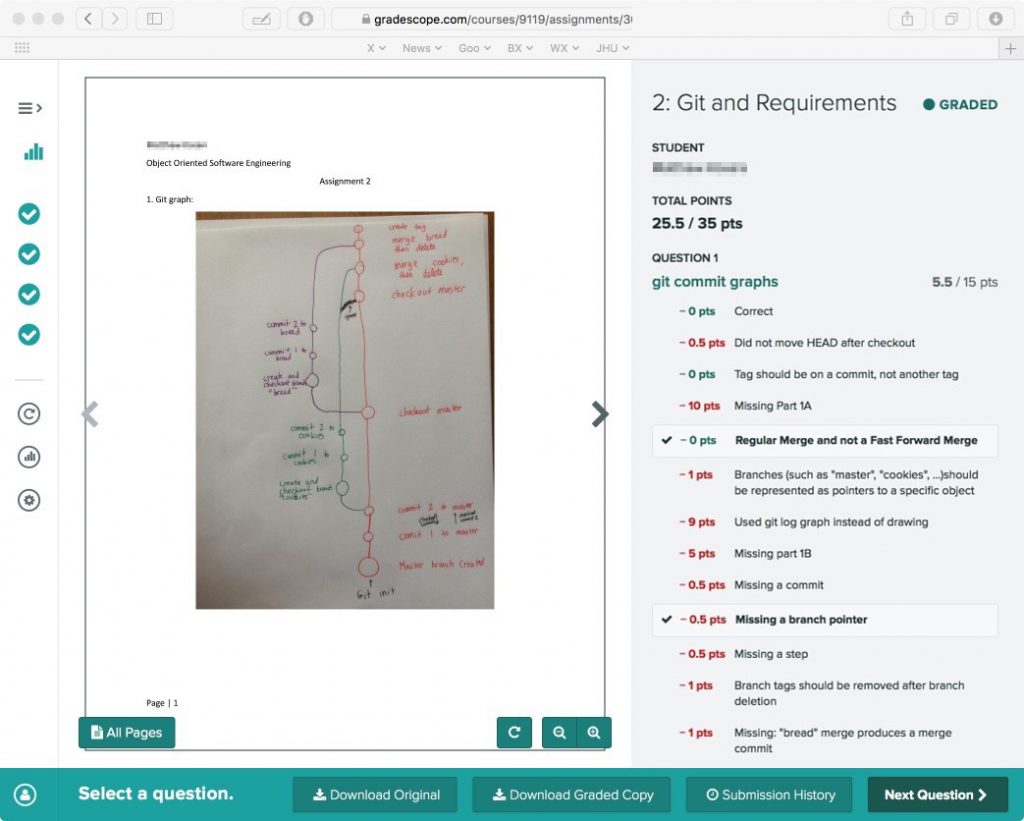
 Grading can be one of the most time consuming and tedious aspects of teaching a course, but it’s important to give prompt and meaningful feedback to your students. In large courses, aligning grading practices across multiple teaching assistants (TAs) necessitates a level of coordination that includes scheduling grading meetings, reviewing materials for correct answers, and calibrating point evaluations, all of which can take up valuable time during the semester.
Grading can be one of the most time consuming and tedious aspects of teaching a course, but it’s important to give prompt and meaningful feedback to your students. In large courses, aligning grading practices across multiple teaching assistants (TAs) necessitates a level of coordination that includes scheduling grading meetings, reviewing materials for correct answers, and calibrating point evaluations, all of which can take up valuable time during the semester.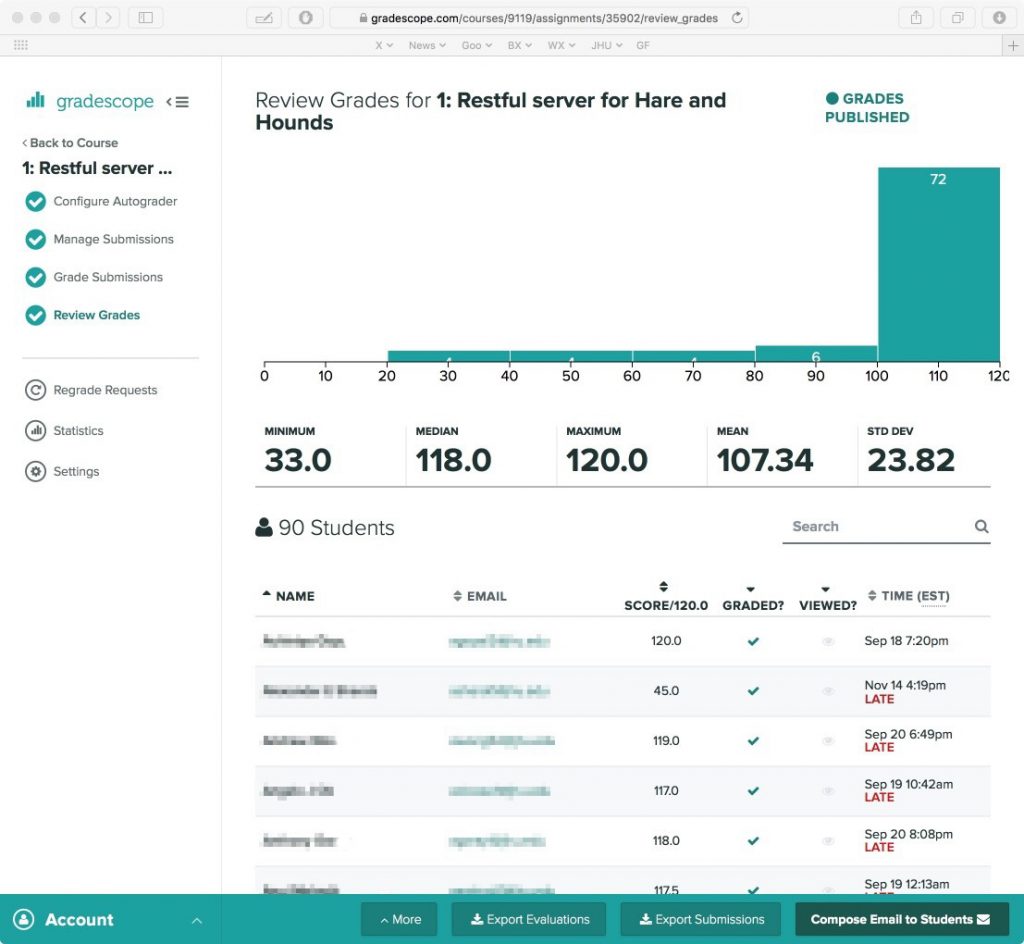
 Innovative Instructor post
Innovative Instructor post  Burger is the co-author of a book, The Five Elements of Effective Thinking, with Michael Starbird [Princeton University Press, 2012]. Burger and Starbird describe five elements that characterize effective thinking: understanding deeply, failing in order to succeed, raising questions, seeing the flow of ideas, and engaging change. A
Burger is the co-author of a book, The Five Elements of Effective Thinking, with Michael Starbird [Princeton University Press, 2012]. Burger and Starbird describe five elements that characterize effective thinking: understanding deeply, failing in order to succeed, raising questions, seeing the flow of ideas, and engaging change. A  In order to keep the readers of The Innovative Instructor informed, I follow a number of blogs and read a lot of books and articles on pedagogy and instruction in higher education. Recently I became aware of a new-to-me resource that I’d like to share, the STEM|PROF weekly newsletter.
In order to keep the readers of The Innovative Instructor informed, I follow a number of blogs and read a lot of books and articles on pedagogy and instruction in higher education. Recently I became aware of a new-to-me resource that I’d like to share, the STEM|PROF weekly newsletter.