On Tuesday, March 12th, the Center for Teaching Excellence and Innovation (CTEI) hosted a Lunch and Learn on Active Learning Techniques: Advice and Guidance from Experienced Faculty. Faculty panelists included Nate Brown, Senior Lecturer, University Writing Program (KSAS); Robert Leheny, Professor and Department Chair, Department of Physics and Astronomy (KSAS); and Michael Falk, Vice Dean of Undergraduate Education and Professor, Department of Materials Science and Engineering (WSE). Caroline Egan, Teaching Academy Program Manager, moderated the discussion.
Nate Brown, Senior Lecturer, University Writing Program (KSAS); Robert Leheny, Professor and Department Chair, Department of Physics and Astronomy (KSAS); and Michael Falk, Vice Dean of Undergraduate Education and Professor, Department of Materials Science and Engineering (WSE). Caroline Egan, Teaching Academy Program Manager, moderated the discussion.
Caroline began the session by asking panelists how they got started with active learning and what they would recommend to those who were thinking about implementing it.
Nate Brown described how he heavily relied on his lecture notes to deliver content to students when he first started teaching. As he’s gained more experience, he’s moved away from using lecture notes and actively involves students in their learning. Brown structures his classes now in such a way that the students drive the conversation and solve problems collectively, leading to greater retention of information and increased engagement. He makes a point of having students think about “why they are doing what they are doing.”
Robert Leheny recalled how the Provost’s Gateway Sciences Initiative from several years ago provided funding to support the redesign of gateway science courses, such as the Introduction to Physics course, which he teaches. The goal of the Gateway Sciences Initiative was to evolve the pedagogy in large introductory science courses to produce better student outcomes.
The Intro to Physics redesign, which was modeled after similar large lecture style courses at NC State and MIT, moved away from a traditional lecture style to a much more interactive experience. Students are divided into groups and sit at round tables instead of in rows, and they solve problem sets together during class rather than at home. This in-class work is partly enabled by a flipped classroom approach which enables students to review the content before coming to class. Leheny said the department now offers two versions of Introduction to Physics that students can select from: an active learning style and a more traditional auditorium/lecture style.
Michael Falk first started implementing active learning by using clickers in a 200-student Introduction to Computer Programming course at the University of Michigan several years ago. Since he’s been at Hopkins, his classes have been smaller, allowing him to approach active learning in different ways. Falk gave an example of how he flipped an upper-level materials science course (which is now also part of the Gateway Computing program) so that students work in an online textbook outside of class and do more collaborative work during class. Another example is a First-Year Seminar class taught by Falk, Turing’s Shadow: Uncovering What’s Hidden in STEM. This discussion-based course covers a range of topics, some of which are sensitive, and students are often afraid to speak up. To address this, Falk created a series of discussion cards to help ease students’ discomfort. The cards provide discussion prompts for students, such as “Clarification: Ask for further explanation about something,” and they also inject some fun elements into the conversation by asking respondents to present their response “in the form of a song,” or “while walking around the room very quickly,” for example. It turns the exercise into a game and helps students to feel more comfortable participating in class.
This discussion-based course covers a range of topics, some of which are sensitive, and students are often afraid to speak up. To address this, Falk created a series of discussion cards to help ease students’ discomfort. The cards provide discussion prompts for students, such as “Clarification: Ask for further explanation about something,” and they also inject some fun elements into the conversation by asking respondents to present their response “in the form of a song,” or “while walking around the room very quickly,” for example. It turns the exercise into a game and helps students to feel more comfortable participating in class.
Caroline continued by asking the panelists what their definition of active learning is and to provide a counter-example of it, which would bring its definition into better relief.
NB: I think it involves giving students a stake in what we’re doing. For example, helping to define the parameters of a paper we’re going to write. I see the professorial role as one of support, like “air traffic control.” With active learning, students are involved in the creation of their own learning.
RL: The primary component of active learning in physics is peer instruction. Students need to be able to solve problems. We don’t use class time to introduce students to concepts, but instead give students an opportunity to practice solving problems where there are resources to help facilitate these skills. For example, students are divided into groups of three and explain to each other how they would go about solving a problem. The act of explaining the problem to someone else helps to solidify their own understanding. A counter example would be the old way of the instructor speaking from the blackboard, talking uninterrupted for most of the class period.
MF: Active learning is learning by doing. Students are engaging with content in a supportive environment. We are teaching a different group of students at Hopkins now – there are many more first- generation, limited-income, and/or underrepresented students with very different backgrounds. We need to think proactively about leveling the playing field for students. This is evident in the data around class outcomes: classes taught using active learning techniques have lower levels of students failing or dropping out. This is even more true for students in underrepresented groups.
RL: We also see this in Intro to Physics. We have the two versions of the course: one in the auditorium (which may have some active learning elements in it), and one designed specifically as an active learning course. The homework and exams are the same in both courses. The outcomes show that failing grades are much less likely to occur in the active learning course.
The homework and exams are the same in both courses. The outcomes show that failing grades are much less likely to occur in the active learning course.
MF: I used to think my job as an instructor was to deliver content and material. Now, with active learning, I think my job is to deliver an experience.
Caroline continued by asking panelists for a simple active learning technique that instructors can implement right away.
NB: This may sound crazy – it comes from a writer colleague of mine. I was having students read out loud in class and noticed they were struggling: they didn’t feel comfortable, they were shy, or were experiencing language barriers, etc. I then asked them all to read in chorus (at the same time). No one understood what they were hearing, but it shocked them into it being ok to share. It really helped them get over their nerves.
RL: Think-Pair-Share. This technique works very well in a large lecture environment. We give students a multiple choice question and have everyone vote on the answer. Next, they have to find someone who voted differently and try to convince them to change their answer. We then ask students to vote again. The results are that there are usually more correct answers the second time. You do need good questions for this to be effective.
MF: An idea for STEM classes, figure out a way to shorten your lecture and hand out the problem set at the end of class. Allow students to work on them with each other. Ask students to write down the steps on how they would solve the problem, but not actually solve it. Allow time for a report out at the end. This gives them a chance to support each other while organizing information.
CE: A complimentary Humanities example: In my first-year writing class, I hand out labeled strips of paper to students with our class readings on them and ask them to organize the strips in a way that would help the students use the readings in their papers. Also, I give students writing prompts, break them into groups, and ask them to find out where they would find the answers to the prompts. This helps to get them in the right mindset of locating good sources.
Two other examples of active learning were mentioned by faculty guests. One instructor explained how she has students use Legos to construct the analysis of an argument. They connect more and more Legos to build supportive elements of their argument and take away those that they disagree with. Another instructor mentioned that she has students act out responses in class.
Legos to construct the analysis of an argument. They connect more and more Legos to build supportive elements of their argument and take away those that they disagree with. Another instructor mentioned that she has students act out responses in class.
The session continued with questions from the audience for the panelists:
Q: In reference to Think-Pair-Share, have you observed any competitiveness among students or reluctance to participate in these activities?
MF: We tell students it has nothing to do with their grade.
RL: We do the same. We also tell them there is no curve and it is possible for everyone to get an A, which reduces overall competitiveness.
NB: One of the great things about this exercise, where students are engaging with each other, is that they get to hear from peers that are from all over the world. We turn it into a social space where they can feel comfortable sharing.
Q: (From a librarian) I recently had about 30 minutes to work with students in a research class. I received feedback from a student that I didn’t do enough active learning in the class, despite doing a brainstorming exercise with them. What do you do when you need more active learning in such a short amount of time?
RL: Explain to students why you structured the class like you did. It will help if you get their buy-in. Maybe the answer is to announce at the beginning that what you’re doing is in fact active leaning.
MF: Students like playing – it makes for a positive learning experience. Perhaps turn part of it into a game/play. And then explain what and why you’re doing it this way.
Q: Are there any active learning experiences to share when you’re guest lecturing? Do you use the same or different strategies?
MF: It needs to be a different strategy. As a guest, you don’t have the advantage of repetition or control of the environment. Explain to students what you’re doing and do the best you can with the constraints that you’re under.
CE: Be very intentional about your choices. At the end, ask them one thing they will remember from the class. This is a good recall exercise.
NB: As a guest speaker, you already are a bit novel since your presence is different than their regular day. Maybe use a novel activity that they will remember.
Q: Could you each share how you put groups together intentionally instead of having students self-form?
RL: Students are put into groups of three. Groups are engineered this way – we switch a few times during the semester. The students don’t know it, but we add them to groups according to their performance on the midterm. In each group, there is one person that scored at the top, one from the middle, and one from a low level. The top level person gets more practice articulating ideas. The lower level person gets the benefit of working with someone who has command of the material. We also group according to gender: we avoid placing two men and one woman in a group to avoid women being excluded. There is research that supports this.
NB: We also do a lot of group work. Halfway through the semester, I ask students to work with someone they haven’t worked with before. I also ask them to sit next to someone different. It results in a richer peer review experience.
MF: I have students do a self-assessment at the very beginning of the course and use the results of the assessment to group students.
For more information about the active learning topics discussed at the event, please see this Active Learning For Distribution folder of materials developed by Caroline Egan.
Amy Brusini, Senior Instructional Designer
Center for Teaching Excellence and Innovation
Image source: Lunch and Learn logo, Unsplash, Pixabay
 Program Manager and Lecturer in the University Writing Program, developed the content and authored the cards. Beth Hals, Senior Instructional Technologist in the CTEI, created the online resource as well as the extension elements for each of the strategies. Both Caroline Egan and Beth Hals facilitated the session, which was hybrid, with both in-person and online participants.
Program Manager and Lecturer in the University Writing Program, developed the content and authored the cards. Beth Hals, Senior Instructional Technologist in the CTEI, created the online resource as well as the extension elements for each of the strategies. Both Caroline Egan and Beth Hals facilitated the session, which was hybrid, with both in-person and online participants.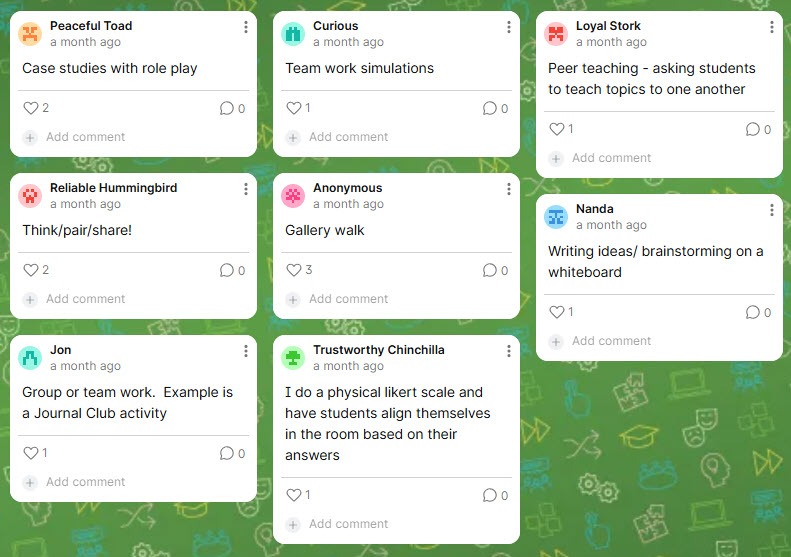 This led to a lively share-out among audience members who were interested in hearing about their peers’ experiences with the strategies they shared, as well as interest in Padlet. Audience responses included: a gallery walk, think-pair-share, group work, brainstorming, case studies, peer instruction, stations, and a jigsaw activity.
This led to a lively share-out among audience members who were interested in hearing about their peers’ experiences with the strategies they shared, as well as interest in Padlet. Audience responses included: a gallery walk, think-pair-share, group work, brainstorming, case studies, peer instruction, stations, and a jigsaw activity.




 listening to the instructor and taking notes.” Research shows active learning is more effective than lecturing. It helps students learn better through activity and engagement. It falls on a continuum ranging from instructor-focused to student-focused learning. Instructor-focused means high instructor control and low student autonomy. An example of that is an active lecture, where traditional lecturing is interspersed with engaging activities. Student-focused means high student autonomy and low instructor control. Examples include problem-based and project-based learning, which require critical thinking, collaboration, and problem-solving. Shared responsibility is in the middle of the continuum. Examples include structured discussions, guided problem-solving, etc.
listening to the instructor and taking notes.” Research shows active learning is more effective than lecturing. It helps students learn better through activity and engagement. It falls on a continuum ranging from instructor-focused to student-focused learning. Instructor-focused means high instructor control and low student autonomy. An example of that is an active lecture, where traditional lecturing is interspersed with engaging activities. Student-focused means high student autonomy and low instructor control. Examples include problem-based and project-based learning, which require critical thinking, collaboration, and problem-solving. Shared responsibility is in the middle of the continuum. Examples include structured discussions, guided problem-solving, etc. The purpose of learning objectives is to
The purpose of learning objectives is to assessment. Assessment is gathering data about the learning process. It is more than just evaluation, where instructors collect data for the purpose of making evaluative and pass/fail judgments. Assessment helps the faculty member facilitate the learning process for students which includes providing feedback to help them improve.
assessment. Assessment is gathering data about the learning process. It is more than just evaluation, where instructors collect data for the purpose of making evaluative and pass/fail judgments. Assessment helps the faculty member facilitate the learning process for students which includes providing feedback to help them improve.
















 While tracking down some resources for active learning this past week, I stumbled on
While tracking down some resources for active learning this past week, I stumbled on 
