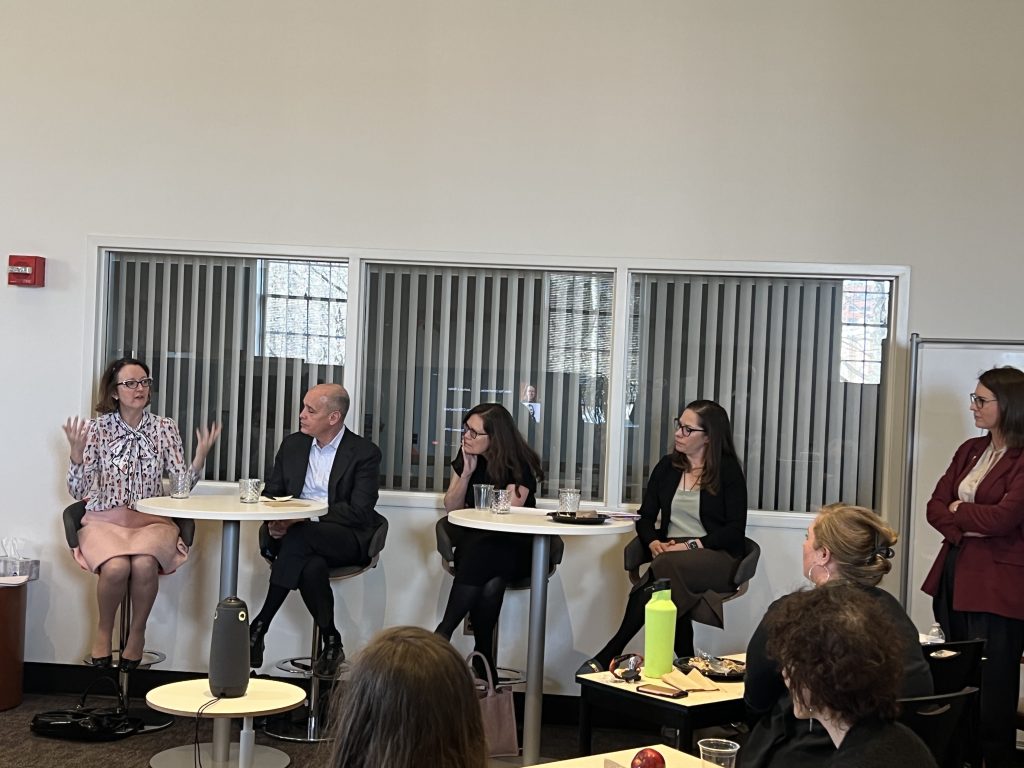
On Wednesday, November 1st, the Center for Teaching Excellence and Innovation (CTEI) hosted a Canvas Show and Tell: Share and Learn about Engaging and Effective Uses of Canvas. Alison Papadakis, Teaching Professor and Director of Clinical Psychological Studies in the Department of Psychological & Brain Sciences, hosted the discussion. She was joined by Emily Braley, Assistant Dean for Undergraduate Academic Affairs and Associate Teaching Professor in the Department of Mathematics, and Jamie Young, Lecturer in the Department of Chemistry. Beth Hals, Brian Cole, and Caroline Egan from the CTEI helped facilitate the event.
On Wednesday, November 1st, the Center for Teaching Excellence and Innovation (CTEI) hosted a Canvas Show and Tell: Share and Learn about Engaging and Effective Uses of Canvas. Alison Papadakis, Teaching Professor and Director of Clinical Psychological Studies in the Department of Psychological & Brain Sciences, hosted the discussion. She was joined by Emily Braley, Assistant Dean for Undergraduate Academic Affairs and Associate Teaching Professor in the Department of Mathematics, and Jamie Young, Lecturer in the Department of Chemistry. Beth Hals, Brian Cole, and Caroline Egan from the CTEI helped facilitate the event.
Alison Papadakis opened the discussion describing how her interest in Canvas began with her kids, who were using it during COVID. (JHU was still using Blackboard at that time.) Watching her kids struggle with poorly designed Canvas classroom interfaces influenced the way she organized her own Canvas classroom once JHU adopted it as our new learning management system (LMS). One big decision she made was to stay away from using the Module function, which is often the most common way to organize content in Canvas. Instead, Papadakis explained how she used the Canvas Page function to create a page with a table outlining her course schedule with hyperlinks to the rest of her content. The homepage of her Canvas site looks like a calendar with hyperlinks for each class day. She regularly checks in with her students, asking if they have trouble finding anything in the course and they always assure her that they do not. Papadakis also makes the Files area in Canvas available to her students, as an additional way for them to access course content, but they tell her they don’t use it. She says the course schedule page is not the “prettiest” display of content, but the functionality works very well for her course and students can easily find what they need for each class period.
Papadakis also does a lot of student advising and needed a place to post links and share information with students. She decided to use a community site, which is similar to a website, but built inside of Canvas. All majors and minors have access to the site as well as other faculty; it is also possible to add other users to the site if necessary. Brian Cole clarified that the key difference between a standard Canvas course and community site is that a standard site is for credited courses and is automatically generated by JHU’s Student Information System (SIS). Community sites, which all faculty have the ability to request, are for non-credit activities and are intended to share information and resources across multiple populations.
Emily Braley described how the mathematics department is using a community site to host their math placement exam. The university’s switch to Canvas provided an opportunity to revise the exam, which was previously hosted in Blackboard. In Canvas, students are provided with more information about why they are taking the exam as they are guided through a series of steps to help them decide which exam to take. With the help of CTEI staff, Braley described how they embedded a Microsoft form inside of Canvas that asks students what math courses they took in high school, including AP courses. The branching feature of the form then directs students to the appropriate placement exam based on their answers. There are also practice tests that students can take before the actual exam.
The exam itself is set up using a Canvas feature called Mastery Paths. This feature allows an instructor to set up to three ranges of scores for the exam; once they take the exam, student scores are translated into a recommendation for enrollment. Braley also created a customized grading scheme for the exam, which contains information about interpreting the results as well as the actual score for the students.
Braley is very excited about the potential for data analytics with the revised exam process. Using the form provides the department with data which can help identify trends and determine if students are being placed correctly. All incoming math students are encouraged to take a math placement exam; so far this fall, close to 1100 students have taken the placement exam.
Jamie Young was looking for a way to avoid having to answer the same questions repeatedly from the 640 students in his Introduction to Chemistry lab course. Using HTML code, he was able to create a dropdown FAQ page in Canvas containing embedded links. He estimates he has received 50-60% less questions this semester so far since posting the FAQ page. He also used HTML to add buttons and links to his syllabus that link out to everything in the course, similar to Alison Papadakis’s course schedule. He believes this saves time for students as they are able to find many things very quickly. Additionally, Young embedded a live Google Document into the course that contains his course schedule. This makes it really easy to update the schedule when necessary as any changes made will immediately be pushed to Canvas – no need to upload an edited document each time a change is made.
In another course, with a combined lecture and lab, Young struggled with displaying a large amount of content. He initially put everything into modules but wasn’t happy with how disorganized they became after adding so much material. He has since turned each module into its own page and links everything from the page. This has been working out much better – again, students are able to find things quickly and easily. Young insists you don’t need much coding knowledge to take advantage of these features in Canvas; you do need to know – or have access to – a few HTML commands.
The discussion included the following questions from the audience:
Q (for Alison Papadakis): Do you need coding experience to create this [the course schedule]?
AP: I just created it in Word and cut and pasted it in – no coding necessary.
Q (for Alison Papadakis): How do you link the “tone” of your course to the course schedule?
AP: This is an in-person course, so there is a lot of in-class discussion around the course and how it works at the beginning. The course schedule is just the pragmatic piece so we can keep things organized.
Q (for Alison Papadakis): It looks like you assign readings before the semester begins – do you plan everything ahead of the semester, before it starts?
AP: I have taught this course over ten times, so I know basically what’s coming. I put placeholders in for things I don’t know yet. You’ll notice it says ‘Tentative Schedule’ so I can allow for shifting things around if needed. I do need to remember to update the Canvas calendar when making changes to my course schedule.
Q (for Alison Papadakis): Can anyone access the community site?
AP: No, they have to be added to the roster.
Q: (For Beth Hals, CTEI’s Sr. Instructional Technologist) Can you explain Mastery Paths? Is it the same as locking/unlocking a Module?
BH: Mastery Paths are affiliated with some sort of assessment in Canvas. As the instructor, you can set three different sets of score ranges that you use to then send students on their next ‘path’ based on their results. Unlocking modules is a little different – you first set prerequisites on a module that must be completed before the module will unlock.
Q (for Jamie Young): To a neophyte, it’s a little overwhelming to see what you’ve done – there seem to be many ways of doing the same thing. Could you compare and contrast the ways of organizing your syllabus?
JY: You can use the Rich Content Editor (RCE) in Canvas to build your syllabus. If you want to add something like buttons, you would then toggle the RCE to view the HTML editor. Using HTML is more complicated for sure, but with some basic knowledge you can do it. I would be happy to share what I’ve done and then you can just fill in your information and cut and paste it into your course. To embed the Google Form, I followed online directions that I googled.
Brian Cole, CTEI’s Associate Director for Instructional Technology: You don’t need any HTML knowledge to embed anything into Canvas. You can use the Rich Content Editor (RCE) to do this. There is an “embed” option in the menu of the editor. You also don’t have to do every page. You can pick and choose what parts of your course to make pretty.
Q: Did Jamie build his syllabus in AEFIS?
BC: No, Jamie built his syllabus using the Canvas Syllabus page. You can still use your own syllabus in conjunction with the AEFIS syllabus – they can coexist. (Note: New name for AEFIS is Heliocampus.)
Q (for Jamie Young): Could you provide a little more information on creating tabs?
JY: They are just HTML code. I used HTML 5. You have to go into the HTML editor in Canvas and use “div” tags to build tabs. Start with the blank tabs in html, then go back to the RCE and fill in the text as needed. You can use copy and paste to make it easier.
Q: Can I move JavaScript headers into Canvas?
BC: No, Canvas will strip them out. An alternative is to embed the page into the Canvas page.
BH: There is something called the Redirect tool that may help. This tool adds an item to your navigational menu. You pick the text for what will display in your menu and it will link to a particular page.
Q: Any ideas about making grading easier?
EB: We use auto grading on all quizzes. We also use banks of questions, so that each quiz pulls from different banks. New Quizzes has matching question types that are more work for students, more robust, but still auto graded. Another thing about New Quizzes is the ability to render Latex [a typesetting software for math symbols]. This has been very useful for us – it’s so much cleaner for students. It renders as accessible MathML, which can be read by a screen reader. This is much better than posting a PDF that is read as an image.
We also use Gradescope, which is an external tool that helps us streamline grading. Students upload their work to Gradescope (inside of Canvas) and you can set it up to help auto grade problems.
JY: We also use Gradescope extensively in Chemistry. We scan written work into Gradescope and it is automatically graded. The system has gotten better at reading handwriting. It has made handwritten assignments so much easier to grade. One caveat about Canvas quizzes: they don’t allow for numbers past 4 decimal places, which we need.
A word about accessibility in Canvas:
EB: You can have Canvas tell you if your material is accessible or not. Use the accessibility checker in the RCE to help you with this.
BH: I also wanted to mention that it’s very easy to duplicate pages in Canvas – build it once, duplicate the page, then fill in what you need to change. It’s like building a template for yourself and reusing it.
For more information about topics discussed at the event, please see this Canvas resource developed by Beth Hals.
Amy Brusini, Senior Instructional Designer
Center for Teaching Excellence and Innovation
Image source: Canvas logo